This class implements the linear time Maximum Mean Statistic as described in [1]. This statistic is in particular suitable for streaming data. Therefore, only streaming features may be passed. To process other feature types, construct streaming features from these (see constructor documentations). A blocksize has to be specified that determines how many examples are processed at once. This should be set as large as available memory allows to ensure faster computations.
The MMD is the distance of two probability distributions 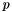 and
and 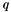 in a RKHS.
in a RKHS.
![\[ \text{MMD}}[\mathcal{F},p,q]^2=\textbf{E}_{x,x'}\left[ k(x,x')\right]- 2\textbf{E}_{x,y}\left[ k(x,y)\right] +\textbf{E}_{y,y'}\left[ k(y,y')\right]=||\mu_p - \mu_q||^2_\mathcal{F} \]](form_313.png)
Given two sets of samples 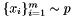 and
and 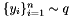 the (unbiased) statistic is computed as
the (unbiased) statistic is computed as
![\[ \text{MMD}_l^2[\mathcal{F},X,Y]=\frac{1}{m_2}\sum_{i=1}^{m_2} h(z_{2i},z_{2i+1}) \]](form_316.png)
where
![\[ h(z_{2i},z_{2i+1})=k(x_{2i},x_{2i+1})+k(y_{2i},y_{2i+1})-k(x_{2i},y_{2i+1})- k(x_{2i+1},y_{2i}) \]](form_317.png)
and 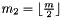 .
.
Along with the statistic comes a method to compute a p-value based on a Gaussian approximation of the null-distribution which is also possible in linear time and constant space. Bootstrapping, is also possible (no permutations but new examples will be used here). If unsure which one to use, bootstrapping with 250 iterations always is correct (but slow). When the sample size is large (>1000) at least, the Gaussian approximation is an accurate and much faster choice than bootstrapping.
To choose, use set_null_approximation_method() and choose from
MMD1_GAUSSIAN: Approximates the null-distribution with a Gaussian. Only use from at least 1000 samples.
BOOTSTRAPPING: For permuting available samples to sample null-distribution
Comes with a method for selecting kernel weights, if a combined kernel on combined features is used. See optimize_kernel_weights(). See [2]
A very basic method for kernel selection when using CGaussianKernel is to use the median distance of the underlying data. See examples how to do that. More advanced methods will follow in the near future. However, the median heuristic works in quite some cases. See [1].
[1]: Gretton, A., Borgwardt, K. M., Rasch, M. J., Schoelkopf, B., & Smola, A. (2012). A Kernel Two-Sample Test. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 13, 671-721.
[2]: Gretton, A., Sriperumbudur, B., Sejdinovic, D., Strathmann, H., Balakrishnan, S., Pontil, M., & Fukumizu, K. (2012). Optimal kernel choice for large-scale two-sample tests. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.
Definition at line 85 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
| CLinearTimeMMD | ( | ) |
Definition at line 21 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
| CLinearTimeMMD | ( | CKernel * | kernel, | |
| CStreamingFeatures * | p, | |||
| CStreamingFeatures * | q, | |||
| index_t | m, | |||
| index_t | blocksize = 10000 | |||
| ) |
Constructor.
| kernel | kernel to use | |
| p | streaming features p to use | |
| q | streaming features q to use | |
| blocksize | size of examples that are processed at once when computing statistic/threshold. If larger than m/2, all examples will be processed at once. Memory consumption increased linearly in the blocksize. Choose as large as possible regarding available memory. |
Definition at line 27 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
| ~CLinearTimeMMD | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Definition at line 42 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
Mimics bootstrapping for the linear time MMD. However, samples are not permutated but constantly streamed and then merged. Usually, this is not necessary since there is the Gaussian approximation for the null distribution. However, in certain cases this may fail and sampling the null distribution might be numerically more stable. Ovewrite superclass method that merges samples.
Reimplemented from CKernelTwoSampleTestStatistic.
Definition at line 275 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
| void build_parameter_dictionary | ( | CMap< TParameter *, CSGObject * > & | dict | ) | [inherited] |
Builds a dictionary of all parameters in SGObject as well of those of SGObjects that are parameters of this object. Dictionary maps parameters to the objects that own them.
| dict | dictionary of parameters to be built. |
Definition at line 1201 of file SGObject.cpp.
computes a p-value based on current method for approximating the null-distribution. The p-value is the 1-p quantile of the null- distribution where the given statistic lies in.
The method for computing the p-value can be set via set_null_approximation_method(). Since the null- distribution is normal, a Gaussian approximation is available.
| statistic | statistic value to compute the p-value for |
Reimplemented from CTwoDistributionsTestStatistic.
Definition at line 201 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
| float64_t compute_statistic | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Computes the squared linear time MMD for the current data. This is an unbiased estimate.
Note that the underlying streaming feature parser has to be started before this is called. Otherwise deadlock.
Implements CTestStatistic.
Definition at line 179 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
Computes MMD and a linear time variance estimate using an in-place method.
| statistic | return parameter for statistic | |
| variance | return parameter for variance |
Definition at line 75 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
computes a threshold based on current method for approximating the null-distribution. The threshold is the value that a statistic has to have in ordner to reject the null-hypothesis.
The method for computing the p-value can be set via set_null_approximation_method(). Since the null- distribution is normal, a Gaussian approximation is available.
| alpha | test level to reject null-hypothesis |
Reimplemented from CTwoDistributionsTestStatistic.
Definition at line 224 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
| float64_t compute_variance_estimate | ( | ) | [virtual] |
computes a linear time estimate of the variance of the squared linear time mmd, which may be used for an approximation of the null-distribution The value is the variance of the vector of which the linear time MMD is the mean.
Definition at line 190 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
| virtual CSGObject* deep_copy | ( | ) | const [virtual, inherited] |
A deep copy. All the instance variables will also be copied.
Definition at line 131 of file SGObject.h.
| SGIO * get_global_io | ( | ) | [inherited] |
| Parallel * get_global_parallel | ( | ) | [inherited] |
| Version * get_global_version | ( | ) | [inherited] |
| SGStringList< char > get_modelsel_names | ( | ) | [inherited] |
Definition at line 1108 of file SGObject.cpp.
| char * get_modsel_param_descr | ( | const char * | param_name | ) | [inherited] |
Returns description of a given parameter string, if it exists. SG_ERROR otherwise
| param_name | name of the parameter |
Definition at line 1132 of file SGObject.cpp.
| index_t get_modsel_param_index | ( | const char * | param_name | ) | [inherited] |
Returns index of model selection parameter with provided index
| param_name | name of model selection parameter |
Definition at line 1145 of file SGObject.cpp.
| virtual const char* get_name | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Returns the name of the SGSerializable instance. It MUST BE the CLASS NAME without the prefixed `C'.
Implements CKernelTwoSampleTestStatistic.
Definition at line 234 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
| const float64_t * get_Q_col | ( | uint32_t | i | ) | [static] |
return pointer to i-th column of m_Q. Helper for libqp
Definition at line 488 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
| bool is_generic | ( | EPrimitiveType * | generic | ) | const [virtual, inherited] |
If the SGSerializable is a class template then TRUE will be returned and GENERIC is set to the type of the generic.
| generic | set to the type of the generic if returning TRUE |
Definition at line 278 of file SGObject.cpp.
| DynArray< TParameter * > * load_all_file_parameters | ( | int32_t | file_version, | |
| int32_t | current_version, | |||
| CSerializableFile * | file, | |||
| const char * | prefix = "" | |||
| ) | [inherited] |
maps all parameters of this instance to the provided file version and loads all parameter data from the file into an array, which is sorted (basically calls load_file_parameter(...) for all parameters and puts all results into a sorted array)
| file_version | parameter version of the file | |
| current_version | version from which mapping begins (you want to use VERSION_PARAMETER for this in most cases) | |
| file | file to load from | |
| prefix | prefix for members |
Definition at line 679 of file SGObject.cpp.
| DynArray< TParameter * > * load_file_parameters | ( | const SGParamInfo * | param_info, | |
| int32_t | file_version, | |||
| CSerializableFile * | file, | |||
| const char * | prefix = "" | |||
| ) | [inherited] |
loads some specified parameters from a file with a specified version The provided parameter info has a version which is recursively mapped until the file parameter version is reached. Note that there may be possibly multiple parameters in the mapping, therefore, a set of TParameter instances is returned
| param_info | information of parameter | |
| file_version | parameter version of the file, must be <= provided parameter version | |
| file | file to load from | |
| prefix | prefix for members |
Definition at line 523 of file SGObject.cpp.
| bool load_serializable | ( | CSerializableFile * | file, | |
| const char * | prefix = "", |
|||
| int32_t | param_version = VERSION_PARAMETER | |||
| ) | [virtual, inherited] |
Load this object from file. If it will fail (returning FALSE) then this object will contain inconsistent data and should not be used!
| file | where to load from | |
| prefix | prefix for members | |
| param_version | (optional) a parameter version different to (this is mainly for testing, better do not use) |
Reimplemented in CModelSelectionParameters.
Definition at line 354 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void load_serializable_post | ( | ) | throw (ShogunException) [protected, virtual, inherited] |
Can (optionally) be overridden to post-initialize some member variables which are not PARAMETER::ADD'ed. Make sure that at first the overridden method BASE_CLASS::LOAD_SERIALIZABLE_POST is called.
| ShogunException | Will be thrown if an error occurres. |
Reimplemented in CLinearHMM, CAlphabet, CANOVAKernel, CCircularKernel, CExponentialKernel, CGaussianKernel, CInverseMultiQuadricKernel, CKernel, CWeightedDegreePositionStringKernel, and CList.
Definition at line 1033 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void load_serializable_pre | ( | ) | throw (ShogunException) [protected, virtual, inherited] |
Can (optionally) be overridden to pre-initialize some member variables which are not PARAMETER::ADD'ed. Make sure that at first the overridden method BASE_CLASS::LOAD_SERIALIZABLE_PRE is called.
| ShogunException | Will be thrown if an error occurres. |
Definition at line 1028 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void map_parameters | ( | DynArray< TParameter * > * | param_base, | |
| int32_t & | base_version, | |||
| DynArray< const SGParamInfo * > * | target_param_infos | |||
| ) | [inherited] |
Takes a set of TParameter instances (base) with a certain version and a set of target parameter infos and recursively maps the base level wise to the current version using CSGObject::migrate(...). The base is replaced. After this call, the base version containing parameters should be of same version/type as the initial target parameter infos. Note for this to work, the migrate methods and all the internal parameter mappings have to match
| param_base | set of TParameter instances that are mapped to the provided target parameter infos | |
| base_version | version of the parameter base | |
| target_param_infos | set of SGParamInfo instances that specify the target parameter base |
Definition at line 717 of file SGObject.cpp.
| TParameter * migrate | ( | DynArray< TParameter * > * | param_base, | |
| const SGParamInfo * | target | |||
| ) | [protected, virtual, inherited] |
creates a new TParameter instance, which contains migrated data from the version that is provided. The provided parameter data base is used for migration, this base is a collection of all parameter data of the previous version. Migration is done FROM the data in param_base TO the provided param info Migration is always one version step. Method has to be implemented in subclasses, if no match is found, base method has to be called.
If there is an element in the param_base which equals the target, a copy of the element is returned. This represents the case when nothing has changed and therefore, the migrate method is not overloaded in a subclass
| param_base | set of TParameter instances to use for migration | |
| target | parameter info for the resulting TParameter |
Definition at line 923 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void one_to_one_migration_prepare | ( | DynArray< TParameter * > * | param_base, | |
| const SGParamInfo * | target, | |||
| TParameter *& | replacement, | |||
| TParameter *& | to_migrate, | |||
| char * | old_name = NULL | |||
| ) | [protected, virtual, inherited] |
This method prepares everything for a one-to-one parameter migration. One to one here means that only ONE element of the parameter base is needed for the migration (the one with the same name as the target). Data is allocated for the target (in the type as provided in the target SGParamInfo), and a corresponding new TParameter instance is written to replacement. The to_migrate pointer points to the single needed TParameter instance needed for migration. If a name change happened, the old name may be specified by old_name. In addition, the m_delete_data flag of to_migrate is set to true. So if you want to migrate data, the only thing to do after this call is converting the data in the m_parameter fields. If unsure how to use - have a look into an example for this. (base_migration_type_conversion.cpp for example)
| param_base | set of TParameter instances to use for migration | |
| target | parameter info for the resulting TParameter | |
| replacement | (used as output) here the TParameter instance which is returned by migration is created into | |
| to_migrate | the only source that is used for migration | |
| old_name | with this parameter, a name change may be specified |
Definition at line 864 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void optimize_kernel_weights | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Selects optimal kernel weights (if the underlying kernel and features are combined ones) using the ratio of the squared MMD by its standard deviation as a criterion, i.e.
![\[ \frac{\text{MMD}_l^2[\mathcal{F},X,Y]}{\sigma_l} \]](form_319.png)
where both expressions are estimated in linear time. This comes down to solving a convex program which is quadratic in the number of kernels.
SHOGUN has to be compiled with LAPACK to make this available. See set_opt* methods for optimization parameters.
IMPORTANT: Kernel weights have to be learned on different data than is used for testing/evaluation!
TODO check whether other types of combined kernels/features might be allowed
Definition at line 311 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
| bool perform_test | ( | float64_t | alpha | ) | [inherited] |
Performs the complete two-sample test on current data and returns a binary answer wheter null hypothesis is rejected or not.
This is just a wrapper for the above perform_test() method that returns a p-value. If this p-value lies below the test level alpha, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Should not be overwritten in subclasses. (Therefore not virtual)
| alpha | test level alpha. |
Definition at line 58 of file TestStatistic.cpp.
| float64_t perform_test | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Performs the complete two-sample test on current data and returns a p-value.
In case null distribution should be estimated with MMD1_GAUSSIAN, statistic and p-value are computed in the same loop, which is more efficient than first computing statistic and then computung p-values.
In case of bootstrapping, superclass method is called.
The method for computing the p-value can be set via set_null_approximation_method().
Reimplemented from CTestStatistic.
Definition at line 247 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
| void print_modsel_params | ( | ) | [inherited] |
prints all parameter registered for model selection and their type
Definition at line 1084 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void print_serializable | ( | const char * | prefix = "" |
) | [virtual, inherited] |
prints registered parameters out
| prefix | prefix for members |
Definition at line 290 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void print_state | ( | libqp_state_T | state | ) | [static] |
helper functions that prints current state
Definition at line 493 of file LinearTimeMMD.cpp.
| bool save_serializable | ( | CSerializableFile * | file, | |
| const char * | prefix = "", |
|||
| int32_t | param_version = VERSION_PARAMETER | |||
| ) | [virtual, inherited] |
Save this object to file.
| file | where to save the object; will be closed during returning if PREFIX is an empty string. | |
| prefix | prefix for members | |
| param_version | (optional) a parameter version different to (this is mainly for testing, better do not use) |
Reimplemented in CModelSelectionParameters.
Definition at line 296 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void save_serializable_post | ( | ) | throw (ShogunException) [protected, virtual, inherited] |
Can (optionally) be overridden to post-initialize some member variables which are not PARAMETER::ADD'ed. Make sure that at first the overridden method BASE_CLASS::SAVE_SERIALIZABLE_POST is called.
| ShogunException | Will be thrown if an error occurres. |
Reimplemented in CKernel.
Definition at line 1043 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void save_serializable_pre | ( | ) | throw (ShogunException) [protected, virtual, inherited] |
Can (optionally) be overridden to pre-initialize some member variables which are not PARAMETER::ADD'ed. Make sure that at first the overridden method BASE_CLASS::SAVE_SERIALIZABLE_PRE is called.
| ShogunException | Will be thrown if an error occurres. |
Reimplemented in CKernel.
Definition at line 1038 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void set_bootstrap_iterations | ( | index_t | bootstrap_iterations | ) | [virtual, inherited] |
sets the number of bootstrap iterations for bootstrap_null()
| bootstrap_iterations | how often bootstrapping shall be done |
Definition at line 44 of file TestStatistic.cpp.
| void set_generic< floatmax_t > | ( | ) | [inherited] |
set generic type to T
| void set_global_io | ( | SGIO * | io | ) | [inherited] |
| void set_global_parallel | ( | Parallel * | parallel | ) | [inherited] |
set the parallel object
| parallel | parallel object to use |
Definition at line 230 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void set_global_version | ( | Version * | version | ) | [inherited] |
set the version object
| version | version object to use |
Definition at line 265 of file SGObject.cpp.
| void set_null_approximation_method | ( | ENullApproximationMethod | null_approximation_method | ) | [virtual, inherited] |
sets the method how to approximate the null-distribution
| null_approximation_method | method to use |
Definition at line 38 of file TestStatistic.cpp.
| void set_opt_epsilon | ( | float64_t | opt_epsilon | ) |
Sets the stopping criterion epsilon for optimizing kernel weights
Definition at line 215 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
| void set_opt_low_cut | ( | float64_t | opt_low_cut | ) |
Sets the low cut for optimizing kernel weights (weight below are set to zero
Definition at line 221 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
| void set_opt_max_iterations | ( | index_t | opt_max_iterations | ) |
Sets the max. number of iterations for optimizing kernel weights
Definition at line 209 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
| void set_opt_regularization_eps | ( | float64_t | opt_regularization_eps | ) |
Sets regularization constant. This value is added on diagonal of matrix for optimizing kernel weights
Definition at line 228 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
| void set_p_and_q | ( | CFeatures * | p_and_q | ) | [virtual, inherited] |
Setter for joint features
| p_and_q | joint features from p and q to set |
Definition at line 144 of file TwoDistributionsTestStatistic.cpp.
| virtual CSGObject* shallow_copy | ( | ) | const [virtual, inherited] |
A shallow copy. All the SGObject instance variables will be simply assigned and SG_REF-ed.
Reimplemented in CGaussianKernel.
Definition at line 122 of file SGObject.h.
| void unset_generic | ( | ) | [inherited] |
unset generic type
this has to be called in classes specializing a template class
Definition at line 285 of file SGObject.cpp.
| bool update_parameter_hash | ( | ) | [protected, virtual, inherited] |
Updates the hash of current parameter combination.
Definition at line 237 of file SGObject.cpp.
io
Definition at line 462 of file SGObject.h.
index_t m_blocksize [protected] |
Number of examples processed at once, i.e. in one burst
Definition at line 259 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
index_t m_bootstrap_iterations [protected, inherited] |
number of iterations for bootstrapping null-distributions
Definition at line 129 of file TestStatistic.h.
uint32_t m_hash [inherited] |
Hash of parameter values
Definition at line 480 of file SGObject.h.
underlying kernel
Definition at line 83 of file KernelTwoSampleTestStatistic.h.
defines the first index of samples of q
Definition at line 102 of file TwoDistributionsTestStatistic.h.
Parameter* m_model_selection_parameters [inherited] |
model selection parameters
Definition at line 474 of file SGObject.h.
ENullApproximationMethod m_null_approximation_method [protected, inherited] |
Defines how the the null distribution is approximated
Definition at line 132 of file TestStatistic.h.
float64_t m_opt_epsilon [protected] |
stopping accuracy of qp solver
Definition at line 266 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
float64_t m_opt_low_cut [protected] |
low cut for weights, if weights are under this value, are set to zero
Definition at line 269 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
index_t m_opt_max_iterations [protected] |
maximum number of iterations of qp solver
Definition at line 263 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
float64_t m_opt_regularization_eps [protected] |
regularization epsilon that is added to diagonal of Q matrix
Definition at line 272 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
concatenated samples of the two distributions (two blocks)
Definition at line 99 of file TwoDistributionsTestStatistic.h.
ParameterMap* m_parameter_map [inherited] |
map for different parameter versions
Definition at line 477 of file SGObject.h.
Parameter* m_parameters [inherited] |
parameters
Definition at line 471 of file SGObject.h.
matrix for selection of kernel weights (static because of libqp)
Definition at line 275 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
CStreamingFeatures* m_streaming_p [protected] |
Streaming feature objects that are used instead of merged samples
Definition at line 253 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
CStreamingFeatures* m_streaming_q [protected] |
Streaming feature objects that are used instead of merged samples
Definition at line 256 of file LinearTimeMMD.h.
parallel
Definition at line 465 of file SGObject.h.
version
Definition at line 468 of file SGObject.h.