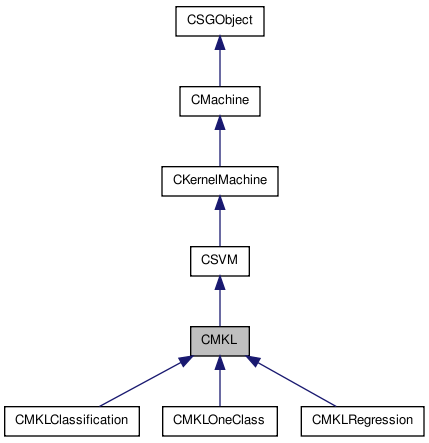
Detailed Description
Multiple Kernel Learning.
A support vector machine based method for use with multiple kernels. In Multiple Kernel Learning (MKL) in addition to the SVM 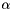 and bias term
and bias term 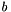 the kernel weights
the kernel weights 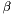 are estimated in training. The resulting kernel method can be stated as
are estimated in training. The resulting kernel method can be stated as
![\[ f({\bf x})=\sum_{i=0}^{N-1} \alpha_i \sum_{j=0}^M \beta_j k_j({\bf x}, {\bf x_i})+b . \]](form_16.png)
where 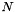 is the number of training examples
is the number of training examples 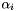 are the weights assigned to each training example
are the weights assigned to each training example 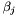 are the weights assigned to each sub-kernel
are the weights assigned to each sub-kernel 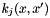 are sub-kernels and
are sub-kernels and 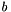 the bias.
the bias.
Kernels have to be chosen a-priori. In MKL 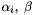 and bias are determined by solving the following optimization program
and bias are determined by solving the following optimization program
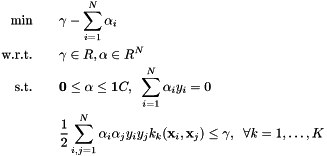
here C is a pre-specified regularization parameter.
Within shogun this optimization problem is solved using semi-infinite programming. For 1-norm MKL using one of the two approaches described in
Soeren Sonnenburg, Gunnar Raetsch, Christin Schaefer, and Bernhard Schoelkopf. Large Scale Multiple Kernel Learning. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 7:1531-1565, July 2006.
The first approach (also called the wrapper algorithm) wraps around a single kernel SVMs, alternatingly solving for 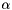 and
and 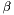 . It is using a traditional SVM to generate new violated constraints and thus requires a single kernel SVM and any of the SVMs contained in shogun can be used. In the MKL step either a linear program is solved via glpk or cplex or analytically or a newton (for norms>1) step is performed.
. It is using a traditional SVM to generate new violated constraints and thus requires a single kernel SVM and any of the SVMs contained in shogun can be used. In the MKL step either a linear program is solved via glpk or cplex or analytically or a newton (for norms>1) step is performed.
The second much faster but also more memory demanding approach performing interleaved optimization, is integrated into the chunking-based SVMlight.
In addition sparsity of MKL can be controlled by the choice of the 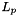 -norm regularizing
-norm regularizing 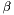 as described in
as described in
Marius Kloft, Ulf Brefeld, Soeren Sonnenburg, and Alexander Zien. Efficient and accurate lp-norm multiple kernel learning. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 21. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 2009.
An alternative way to control the sparsity is the elastic-net regularization, which can be formulated into the following optimization problem:
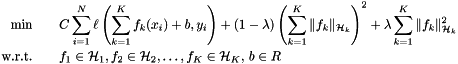
where 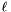 is a loss function. Here
is a loss function. Here 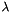 controls the trade-off between the two regularization terms.
controls the trade-off between the two regularization terms. 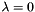 corresponds to
corresponds to 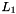 -MKL, whereas
-MKL, whereas 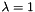 corresponds to the uniform-weighted combination of kernels (
corresponds to the uniform-weighted combination of kernels ( 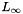 -MKL). This approach was studied by Shawe-Taylor (2008) "Kernel Learning for Novelty Detection" (NIPS MKL Workshop 2008) and Tomioka & Suzuki (2009) "Sparsity-accuracy trade-off in MKL" (NIPS MKL Workshop 2009).
-MKL). This approach was studied by Shawe-Taylor (2008) "Kernel Learning for Novelty Detection" (NIPS MKL Workshop 2008) and Tomioka & Suzuki (2009) "Sparsity-accuracy trade-off in MKL" (NIPS MKL Workshop 2009).
Definition at line 93 of file MKL.h.
List of all members.
Public Member Functions |
| | CMKL (CSVM *s=NULL) |
| virtual | ~CMKL () |
| void | set_constraint_generator (CSVM *s) |
| void | set_svm (CSVM *s) |
| CSVM * | get_svm () |
| void | set_C_mkl (float64_t C) |
| void | set_mkl_norm (float64_t norm) |
| void | set_elasticnet_lambda (float64_t elasticnet_lambda) |
| void | set_mkl_block_norm (float64_t q) |
| void | set_interleaved_optimization_enabled (bool enable) |
| bool | get_interleaved_optimization_enabled () |
| float64_t | compute_mkl_primal_objective () |
| virtual float64_t | compute_mkl_dual_objective () |
| float64_t | compute_elasticnet_dual_objective () |
| void | set_mkl_epsilon (float64_t eps) |
| float64_t | get_mkl_epsilon () |
| int32_t | get_mkl_iterations () |
| virtual bool | perform_mkl_step (const float64_t *sumw, float64_t suma) |
| virtual float64_t | compute_sum_alpha ()=0 |
| virtual void | compute_sum_beta (float64_t *sumw) |
| virtual const char * | get_name () const |
Static Public Member Functions |
| static bool | perform_mkl_step_helper (CMKL *mkl, const float64_t *sumw, const float64_t suma) |
Protected Member Functions |
| virtual bool | train_machine (CFeatures *data=NULL) |
| virtual void | init_training ()=0 |
| void | perform_mkl_step (float64_t *beta, float64_t *old_beta, int num_kernels, int32_t *label, int32_t *active2dnum, float64_t *a, float64_t *lin, float64_t *sumw, int32_t &inner_iters) |
| float64_t | compute_optimal_betas_via_cplex (float64_t *beta, const float64_t *old_beta, int32_t num_kernels, const float64_t *sumw, float64_t suma, int32_t &inner_iters) |
| float64_t | compute_optimal_betas_via_glpk (float64_t *beta, const float64_t *old_beta, int num_kernels, const float64_t *sumw, float64_t suma, int32_t &inner_iters) |
| float64_t | compute_optimal_betas_elasticnet (float64_t *beta, const float64_t *old_beta, const int32_t num_kernels, const float64_t *sumw, const float64_t suma, const float64_t mkl_objective) |
| void | elasticnet_transform (float64_t *beta, float64_t lmd, int32_t len) |
| void | elasticnet_dual (float64_t *ff, float64_t *gg, float64_t *hh, const float64_t &del, const float64_t *nm, int32_t len, const float64_t &lambda) |
| float64_t | compute_optimal_betas_directly (float64_t *beta, const float64_t *old_beta, const int32_t num_kernels, const float64_t *sumw, const float64_t suma, const float64_t mkl_objective) |
| float64_t | compute_optimal_betas_block_norm (float64_t *beta, const float64_t *old_beta, const int32_t num_kernels, const float64_t *sumw, const float64_t suma, const float64_t mkl_objective) |
| float64_t | compute_optimal_betas_newton (float64_t *beta, const float64_t *old_beta, int32_t num_kernels, const float64_t *sumw, float64_t suma, float64_t mkl_objective) |
| virtual bool | converged () |
| void | init_solver () |
| bool | init_cplex () |
| void | set_qnorm_constraints (float64_t *beta, int32_t num_kernels) |
| bool | cleanup_cplex () |
| bool | init_glpk () |
| bool | cleanup_glpk () |
| bool | check_lpx_status (LPX *lp) |
Protected Attributes |
| CSVM * | svm |
| float64_t | C_mkl |
| float64_t | mkl_norm |
| float64_t | ent_lambda |
| float64_t | mkl_block_norm |
| float64_t * | beta_local |
| int32_t | mkl_iterations |
| float64_t | mkl_epsilon |
| bool | interleaved_optimization |
| float64_t * | W |
| float64_t | w_gap |
| float64_t | rho |
| CTime | training_time_clock |
| CPXENVptr | env |
| CPXLPptr | lp_cplex |
| LPX * | lp_glpk |
| bool | lp_initialized |
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
Constructor
- Parameters:
-
| s | SVM to use as constraint generator in MKL SIP |
Definition at line 21 of file MKL.cpp.
Destructor
Definition at line 40 of file MKL.cpp.
Member Function Documentation
| bool check_lpx_status |
( |
LPX * |
lp |
) |
[protected] |
check glpk error status
- Returns:
- if in good status
Definition at line 175 of file MKL.cpp.
| bool cleanup_cplex |
( |
|
) |
[protected] |
cleanup cplex
- Returns:
- if cleanup was successful
Definition at line 119 of file MKL.cpp.
| bool cleanup_glpk |
( |
|
) |
[protected] |
cleanup glpk
- Returns:
- if cleanup was successful
Definition at line 166 of file MKL.cpp.
| float64_t compute_elasticnet_dual_objective |
( |
|
) |
|
compute ElasticnetMKL dual objective
- Returns:
- computed dual objective
Definition at line 581 of file MKL.cpp.
| float64_t compute_mkl_dual_objective |
( |
|
) |
[virtual] |
compute mkl dual objective
- Returns:
- computed dual objective
Reimplemented in CMKLRegression.
Definition at line 1509 of file MKL.cpp.
compute mkl primal objective
- Returns:
- computed mkl primal objective
Definition at line 185 of file MKL.h.
given the alphas, compute the corresponding optimal betas
- Parameters:
-
| beta | new betas (kernel weights) |
| old_beta | old betas (previous kernel weights) |
| num_kernels | number of kernels |
| sumw | 1/2*alpha'*K_j*alpha for each kernel j |
| suma | (sum over alphas) |
| mkl_objective | the current mkl objective |
- Returns:
- new objective value
Definition at line 656 of file MKL.cpp.
given the alphas, compute the corresponding optimal betas
- Parameters:
-
| beta | new betas (kernel weights) |
| old_beta | old betas (previous kernel weights) |
| num_kernels | number of kernels |
| sumw | 1/2*alpha'*K_j*alpha for each kernel j |
| suma | (sum over alphas) |
| mkl_objective | the current mkl objective |
- Returns:
- new objective value
Definition at line 692 of file MKL.cpp.
given the alphas, compute the corresponding optimal betas
- Parameters:
-
| beta | new betas (kernel weights) |
| old_beta | old betas (previous kernel weights) |
| num_kernels | number of kernels |
| sumw | 1/2*alpha'*K_j*alpha for each kernel j |
| suma | (sum over alphas) |
| mkl_objective | the current mkl objective |
- Returns:
- new objective value
Definition at line 462 of file MKL.cpp.
given the alphas, compute the corresponding optimal betas
- Parameters:
-
| beta | new betas (kernel weights) |
| old_beta | old betas (previous kernel weights) |
| num_kernels | number of kernels |
| sumw | 1/2*alpha'*K_j*alpha for each kernel j |
| suma | (sum over alphas) |
| mkl_objective | the current mkl objective |
- Returns:
- new objective value
Definition at line 781 of file MKL.cpp.
given the alphas, compute the corresponding optimal betas using a lp for 1-norm mkl, a qcqp for 2-norm mkl and an iterated qcqp for general q-norm mkl.
- Parameters:
-
| beta | new betas (kernel weights) |
| old_beta | old betas (previous kernel weights) |
| num_kernels | number of kernels |
| sumw | 1/2*alpha'*K_j*alpha for each kernel j |
| suma | (sum over alphas) |
| inner_iters | number of internal iterations (for statistics) |
- Returns:
- new objective value
Definition at line 973 of file MKL.cpp.
given the alphas, compute the corresponding optimal betas using a lp for 1-norm mkl
- Parameters:
-
| beta | new betas (kernel weights) |
| old_beta | old betas (previous kernel weights) |
| num_kernels | number of kernels |
| sumw | 1/2*alpha'*K_j*alpha for each kernel j |
| suma | (sum over alphas) |
| inner_iters | number of internal iterations (for statistics) |
- Returns:
- new objective value
Definition at line 1316 of file MKL.cpp.
| virtual float64_t compute_sum_alpha |
( |
|
) |
[pure virtual] |
| void compute_sum_beta |
( |
float64_t * |
sumw |
) |
[virtual] |
compute 1/2*alpha'*K_j*alpha for each kernel j (beta dependent term from objective)
- Parameters:
-
| sumw | vector of size num_kernels to hold the result |
Definition at line 1466 of file MKL.cpp.
| virtual bool converged |
( |
|
) |
[protected, virtual] |
check if mkl converged, i.e. 'gap' is below epsilon
- Returns:
- whether mkl converged
Definition at line 402 of file MKL.h.
helper function to compute the elastic-net objective
Definition at line 554 of file MKL.cpp.
helper function to compute the elastic-net sub-kernel weights
Definition at line 343 of file MKL.h.
| bool get_interleaved_optimization_enabled |
( |
|
) |
|
get state of optimization (interleaved or wrapper)
- Returns:
- true if interleaved optimization is used; wrapper otherwise
Definition at line 176 of file MKL.h.
get mkl epsilon for weights (optimization accuracy for kernel weights)
- Returns:
- epsilon for weights
Definition at line 213 of file MKL.h.
| int32_t get_mkl_iterations |
( |
|
) |
|
get number of MKL iterations
- Returns:
- mkl_iterations
Definition at line 219 of file MKL.h.
| virtual const char* get_name |
( |
void |
|
) |
const [virtual] |
- Returns:
- object name
Reimplemented from CSVM.
Definition at line 258 of file MKL.h.
get SVM that is used as constraint generator in MKL SIP
- Returns:
- svm
Definition at line 130 of file MKL.h.
| bool init_cplex |
( |
|
) |
[protected] |
init cplex
- Returns:
- if init was successful
Definition at line 70 of file MKL.cpp.
| bool init_glpk |
( |
|
) |
[protected] |
init glpk
- Returns:
- if init was successful
Definition at line 155 of file MKL.cpp.
| void init_solver |
( |
|
) |
[protected] |
initialize solver such as glpk or cplex
Definition at line 52 of file MKL.cpp.
| virtual void init_training |
( |
|
) |
[protected, pure virtual] |
perform single mkl iteration
given sum of alphas, objectives for current alphas for each kernel and current kernel weighting compute the corresponding optimal kernel weighting (all via get/set_subkernel_weights in CCombinedKernel)
- Parameters:
-
| sumw | vector of 1/2*alpha'*K_j*alpha for each kernel j |
| suma | scalar sum_i alpha_i etc. |
Definition at line 395 of file MKL.cpp.
perform single mkl iteration
given the alphas, compute the corresponding optimal betas
- Parameters:
-
| beta | new betas (kernel weights) |
| old_beta | old betas (previous kernel weights) |
| num_kernels | number of kernels |
| label | (from svmlight label) |
| active2dnum | (from svmlight active2dnum) |
| a | (from svmlight alphas) |
| lin | (from svmlight linear components) |
| sumw | 1/2*alpha'*K_j*alpha for each kernel j |
| inner_iters | number of required internal iterations |
callback helper function calling perform_mkl_step
- Parameters:
-
| mkl | MKL object |
| sumw | vector of 1/2*alpha'*K_j*alpha for each kernel j |
| suma | scalar sum_i alpha_i etc. |
Definition at line 239 of file MKL.h.
set C mkl
- Parameters:
-
Definition at line 140 of file MKL.h.
| void set_constraint_generator |
( |
CSVM * |
s |
) |
|
SVM to use as constraint generator in MKL SIP
- Parameters:
-
Definition at line 110 of file MKL.h.
| void set_elasticnet_lambda |
( |
float64_t |
elasticnet_lambda |
) |
|
set elasticnet lambda
- Parameters:
-
| elasticnet_lambda | new elastic net lambda (must be 0<=lambda<=1) lambda=0: L1-MKL lambda=1: Linfinity-MKL |
Definition at line 374 of file MKL.cpp.
| void set_interleaved_optimization_enabled |
( |
bool |
enable |
) |
|
set state of optimization (interleaved or wrapper)
- Parameters:
-
| enable | if true interleaved optimization is used; wrapper otherwise |
Definition at line 167 of file MKL.h.
set block norm q (used in block norm mkl)
- Parameters:
-
Definition at line 387 of file MKL.cpp.
set mkl epsilon (optimization accuracy for kernel weights)
- Parameters:
-
Definition at line 207 of file MKL.h.
set mkl norm
- Parameters:
-
| norm | new mkl norm (must be greater equal 1) |
Definition at line 365 of file MKL.cpp.
| void set_qnorm_constraints |
( |
float64_t * |
beta, |
|
|
int32_t |
num_kernels | |
|
) |
| | [protected] |
set qnorm mkl constraints
Definition at line 1560 of file MKL.cpp.
| void set_svm |
( |
CSVM * |
s |
) |
|
SVM to use as constraint generator in MKL SIP
- Parameters:
-
Definition at line 119 of file MKL.h.
| bool train_machine |
( |
CFeatures * |
data = NULL |
) |
[protected, virtual] |
train MKL classifier
- Parameters:
-
| data | training data (parameter can be avoided if distance or kernel-based classifiers are used and distance/kernels are initialized with train data) |
- Returns:
- whether training was successful
Reimplemented from CMachine.
Definition at line 193 of file MKL.cpp.
Member Data Documentation
sub-kernel weights on the L1-term of ElasticnetMKL
Definition at line 466 of file MKL.h.
C_mkl
Definition at line 451 of file MKL.h.
Sparsity trade-off parameter used in ElasticnetMKL must be 0<=lambda<=1 lambda=0: L1-MKL lambda=1: Linfinity-MKL
Definition at line 459 of file MKL.h.
CPXENVptr env [protected] |
env
Definition at line 487 of file MKL.h.
whether to use mkl wrapper or interleaved opt.
Definition at line 472 of file MKL.h.
lp
Definition at line 489 of file MKL.h.
lp
Definition at line 494 of file MKL.h.
if lp is initialized
Definition at line 497 of file MKL.h.
Sparsity trade-off parameter used in block norm MKL should be 1 <= mkl_block_norm <= inf
Definition at line 463 of file MKL.h.
mkl_epsilon for multiple kernel learning
Definition at line 470 of file MKL.h.
number of mkl steps
Definition at line 468 of file MKL.h.
norm used in mkl must be > 0
Definition at line 453 of file MKL.h.
objective after mkl iterations
Definition at line 480 of file MKL.h.
wrapper SVM
Definition at line 449 of file MKL.h.
partial objectives (one per kernel)
Definition at line 475 of file MKL.h.
gap between iterations
Definition at line 478 of file MKL.h.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
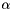 and bias term
and bias term 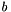 the kernel weights
the kernel weights 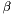 are estimated in training. The resulting kernel method can be stated as
are estimated in training. The resulting kernel method can be stated as![\[ f({\bf x})=\sum_{i=0}^{N-1} \alpha_i \sum_{j=0}^M \beta_j k_j({\bf x}, {\bf x_i})+b . \]](form_16.png)
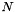 is the number of training examples
is the number of training examples 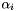 are the weights assigned to each training example
are the weights assigned to each training example 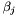 are the weights assigned to each sub-kernel
are the weights assigned to each sub-kernel 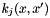 are sub-kernels and
are sub-kernels and 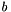 the bias.
the bias.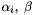 and bias are determined by solving the following optimization program
and bias are determined by solving the following optimization program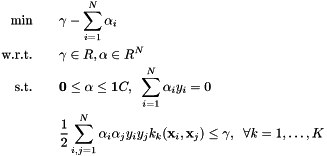
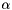 and
and 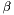 . It is using a traditional SVM to generate new violated constraints and thus requires a single kernel SVM and any of the SVMs contained in shogun can be used. In the MKL step either a linear program is solved via glpk or cplex or analytically or a newton (for norms>1) step is performed.
. It is using a traditional SVM to generate new violated constraints and thus requires a single kernel SVM and any of the SVMs contained in shogun can be used. In the MKL step either a linear program is solved via glpk or cplex or analytically or a newton (for norms>1) step is performed.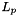 -norm regularizing
-norm regularizing 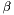 as described in
as described in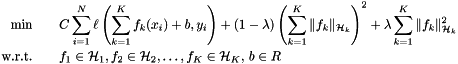
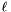 is a loss function. Here
is a loss function. Here 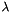 controls the trade-off between the two regularization terms.
controls the trade-off between the two regularization terms. 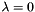 corresponds to
corresponds to 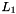 -MKL, whereas
-MKL, whereas 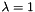 corresponds to the uniform-weighted combination of kernels (
corresponds to the uniform-weighted combination of kernels ( 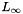 -MKL). This approach was studied by Shawe-Taylor (2008) "Kernel Learning for Novelty Detection" (NIPS MKL Workshop 2008) and Tomioka & Suzuki (2009) "Sparsity-accuracy trade-off in MKL" (NIPS MKL Workshop 2009).
-MKL). This approach was studied by Shawe-Taylor (2008) "Kernel Learning for Novelty Detection" (NIPS MKL Workshop 2008) and Tomioka & Suzuki (2009) "Sparsity-accuracy trade-off in MKL" (NIPS MKL Workshop 2009).